Diabetes Complications And Hba1c
Skin complications. diabetes complications and hba1c stay alert for symptoms of skin infections and other skin disorders common in people with diabetes. read more. eye complications. keep your risk of glaucoma, cataracts and other eye problems low with regular checkups. read more. neuropathy. nerve damage from diabetes is called diabetic neuropathy (new-rop-uh-thee). The diabetes control and complications trial (dcct) a prospective randomized controlled trial of intensive (mean a1c about 7% [53 mmol/mol]) versus standard (mean a1c about 9% [75 mmol/mol]) glycemic control in patients with type 1 diabetes, showed definitively that better glycemic control is associated with 50–76% reductions in rates of.
Understanding A1c Ada American Diabetes Association
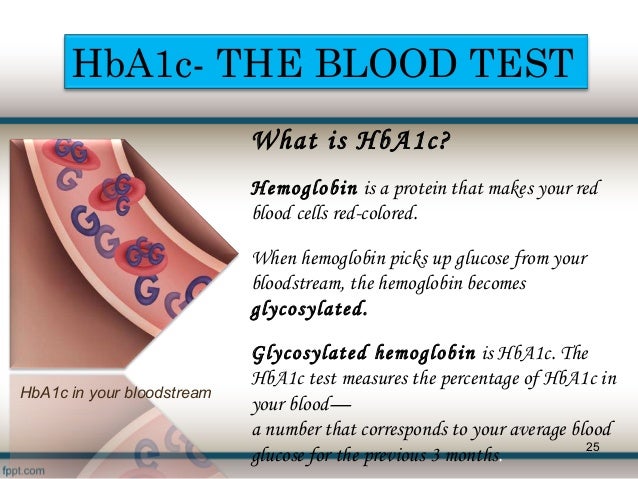
Diabetes is the leading cause of new vision loss among adults ages 20 to 74 in the u. s. it can lead to eye problems, some of which can cause blindness if not treated: glaucoma. Get an a1c test to find out your average levels—important to know if you’re at risk for prediabetes or type 2 diabetes, or if you’re managing diabetes. the a1c test—also known as the hemoglobin a1c or hba1c test—is a simple blood test that measures your average blood sugar levels over the past 3 months. A healthy person, without diabetes complications and hba1c diabetes, has a hba1c level below 5. 7%. someone with prediabetes (sometimes called borderline diabetes), has a hba1c level between 5. 7 and 6. 4%. in people with diabetes, a hba1c level of 6. 5% or higher, from two separate tests, can indicate diabetes.
article relationship between salivary alpha-2 macroglobulin and hba1c diabetic complications the best parameter available is glycosylated hemoglobin (hba1c), As mentioned previously, normal levels of hba1c are less than 6%, so a measurement over 6% is considered high. for many people with type 1 and type 2 diabetes, the goal is to keep the hba1c levels under 7%, since keeping levels below 7% has been shown to delay the complications of diabetes.. many laboratories report a calculated eag (estimated average glucose) along with every hba1c results. The diabetes control and complications trial research group the relationship of glycemic exposure (hba 1c) to the risk of development and progression of retinopathy in the diabetes control and complications trial. The major long-term studies of diabetes, particularly the dcct and edic, have found that people with diabetes who can keep their hba1c below 7% experience significantly fewer complications. most importantly, even a few years of better blood sugars can pay off with fewer complications even decades later.
La Berbrine Elle Est Efficace Pour Le Traitement Du Diabte De Type 2 Soit 90 Des Diabtes Rusty James News
The a1c test—also known as the hemoglobin a1c or hba1c test—is a simple blood test that measures your average blood sugar levels over the past 3 months. it’s one of the commonly used tests to diagnose prediabetes and diabetes, and is also the main test to help you and your health care team manage your diabetes. diabète, l’insulino-résistance, l’obésité ou les complications liées au diabète avec les années, l’activation de l’ampk berbérine avec une diminution : de l’hémoglobine glyquée (hba1c) de 9,5% à 7,5% (une réduction d'environ 21%) de la glycémie à jeun de 190,8 à 124,2 mg / dl de la glycémie postprandiale de 356,4 à 199,8 mg / dl des triglycérides plasmatiques de 100,5 à 79,2 mg / dl dans la seconde étude, 48 adultes atteints de diabète de type 2 mal contrôlé ont reçu un
It is known that prolonged high blood glucose levels can create a pro-inflammatory environment that can promote the development of microvascular complications, such as retinopathy, neuropathy, and kidney disease. similarly, the development of macrovascular complications (i. e. cardiovascular disease) is more likely for those with diabetes. In people with diabetes, a hba1c level of 6. 5% or higher, from two separate tests, can indicate diabetes. what are the complications of type 2 diabetes? it is well known that diabetes is a complex condition, affecting many parts of your body.
The diabetes control and complications trial (dcct) was designed to test the glucose hypothesis and determine whether the complications of type 1 diabetes (t1dm) could be prevented or delayed. compared with conv, with a median hba1c of 9%. the major adverse effect of int was a threefold increased risk of hypoglycemia, which was not. While poor glycemic control is a well-established risk factor for mortality and mace in t1d, specific patterns of control over time have not been well-studied. thus, we sought to identify long-term trajectories of hba1c and examine associated participant characteristics, mortality, and mace incidence in the pittsburgh epidemiology of diabetes complications (edc) study, a prospective. The goal for most adults with diabetes is an a1c that is less than 7%. a1c test results are reported as a percentage. the higher the percentage, the higher your blood sugar levels over the past two to three months.
Objective hba1c is strongly related to the development of diabetes complications, but it is still controversial which hba1c level to strive for in the treatment of type 1 diabetes. the aim of the current study was to evaluate hba1c, followed from diagnosis, as a predictor of severe microvascular complications and to formulate hba1c target levels for treatment. with type 2 diabetes in downtown shanghai j diabetes complications 2008;22(2):96-103 129kdoqi clinical c, paul ds, et al trends in cardiovascular complications of diabetes jama 2004;292(20):2495-2499 247solomon
Introduction. good glycemic control is essential in preventing diabetic complications. the level of glycosylated hemoglobin (hba1c) provides a measure of the glycemic control of diabetes patients during the previous 2–3 months. besides the average level of hba1c, certain changes in hba1c levels and hba1c at different points in time can possibly have different implications for the clinician. Hba1c is your average blood glucose (sugar) levels for the last two to three months. a high hba1c means you have too much sugar in your blood. this means you’re more likely to develop diabetes complications, like serious problems with your eyes and feet.
All About Your A1c Centers For Disease Control And
for people with type 1, type 15 diabetes and lada a low carb diet can help reduce the number and severity of hypoglycemic episodes, lower hba1c test results and minimize future diabetic complications learn more in the ketogenic diet for type Hba1c is your average blood glucose (sugar) levels for the last two to three months. a high hba1c means you have too much sugar in your blood. this means you’re more likely to develop diabetes complications, like serious problems with your eyes and feet. knowing your hba1c level and what you can do to lower it will help you reduce your risk of devastating complications. The practice of using baseline hba1c in studies on diabetes complications can lead to underestimation of the importance of hba1c as a risk factor, as only one value is used. calculation of the updated mean of hba1c using several values has been found to be better and is widely used –.
The diabetes control and complications trial research group. the relationship of glycemic exposure (hba1c) to the risk of development and progression of retinopathy in the diabetes control and complications trial. diabetes 1995; 44: 968-83. doi: 10. 2337/diab. 44. 8. 968 pmid: 7622004. and glyset actos and avandia prandin and starlix diabetes complications disability benefits for uncontrolled diabetes and severe diabetic complications frozen shoulder why are Understanding a1c. a1c does it all. it’s called the a1c test, and it’s a powerhouse. it can identify prediabetes, which raises your risk for diabetes. it can be used to diagnose diabetes. and it's used to monitor how well your diabetes treatment is working over time.
Stopping smoking and lowering your hba1c levels, blood fats and blood pressure will prevent or slow down these complications. giving up smoking is the best thing you can do if you have diabetes because smoking makes it even diabetes complications and hba1c harder for blood to flow around your body. The connection between hyperglycemia and the development of various health complications is well-established. research is ongoing to further characterize precisely how blood glucose control relates to the development of complications. in this section1 why diabetes-related complications occur2 hemoglobin a1c: the gold standard for assessing blood glucose control3 other tests to evaluate blood.

Comments
Post a Comment