Cdc Diabetes Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B Niddk
Acip Hepatitis B Vaccine Recommendations Cdc
Hepatitis b vaccination rate in patients with diabetes.
Oct. 25, 2011 -do you have diabetes? get the hepatitis b vaccine, says the advisory committee on immunization practices (acip).. by a 12-2 vote, the acip strongly recommended the hepatitis b. Chronic hepatitis b is more common in africa, asia, and parts of the middle east, eastern europe, and south and central america than it is in the united states. 7 chronic hepatitis b infection has been especially common in some parts of the world, including sub-saharan africa, parts cdc diabetes hepatitis b of asia, and the pacific islands. 5,8 use of the hepatitis b.
Cdc recommends hepatitis b vaccination for all unvaccinated adults with diabetes who are younger than 60 years of age. many people have had the hepatitis b vaccine as a child, so check with your doctor to see if you have been vaccinated already. Cdc recommends hepatitis b vaccination for all unvaccinated adults with diabetes who are younger than 60 years of age. many people have had the hepatitis b vaccine as a child, so check with your doctor to see if you have been vaccinated already. Outbreaks of hepatitis b associated with blood glucose monitoring procedures have happened among people with diabetes. people with diabetes are at increased risk for death from pneumonia (lung infection), bacteremia (blood infection) and meningitis (infection of the lining of the brain and spinal cord).

The goals of the survey were to determine the level of awareness among diabetes educators of the cdc recommendations to vaccinate adults with diabetes, how diabetes educators typically inform their patients, and what level of awareness exists among aade members' patients about vaccinations, hepatitis b vaccination specifically. support: publichealthcorps ppi heartburn drugs cause dementia, b-12 vitamin deficiency, heart & kidney problems ? mercola’s findings faim foundation for alternative and integrative medicine: recent articles health topics autoimmune diseases autism diabetes glaucoma alzheimer’s diabetes eye health nutrition fatigue Hepatitisb is different: you don’t hear about outbreaks, and infection rates have remained relatively low and stable in the u. s. for decades. but don’t let that fool you; hepatitis b is a.
The centers for disease control and prevention (cdc) uses the 2012 acute hepatitis b case definition to determine the annual reported incidence of hbv infection in the united states. [ 7 8 ] this value is commonly presented as an incidence rate, defined as the number of acute hbv cases per 100,000 persons per year. [ 8 ]. Chronic hepatitis b is more common in africa, asia, and parts of the middle east, eastern europe, and south and central america than it is in the united states. 7 chronic hepatitis b infection has been especially common in some parts of the world, including sub-saharan africa, parts of asia, and the pacific islands. 5,8 use of the hepatitis b vaccine has helped lower infection rates in some of these areas. 7,9. politics propaganda sodom one comment (comments are closed) cdc medical tyranny hepatitis b vaccination for infants ? the cdc’s recommendation for chick-fil-a banned by phony “liberal” establishment… cdc medical tyranny hepatitis b vaccination for infants ? repeal immunity for drug companies
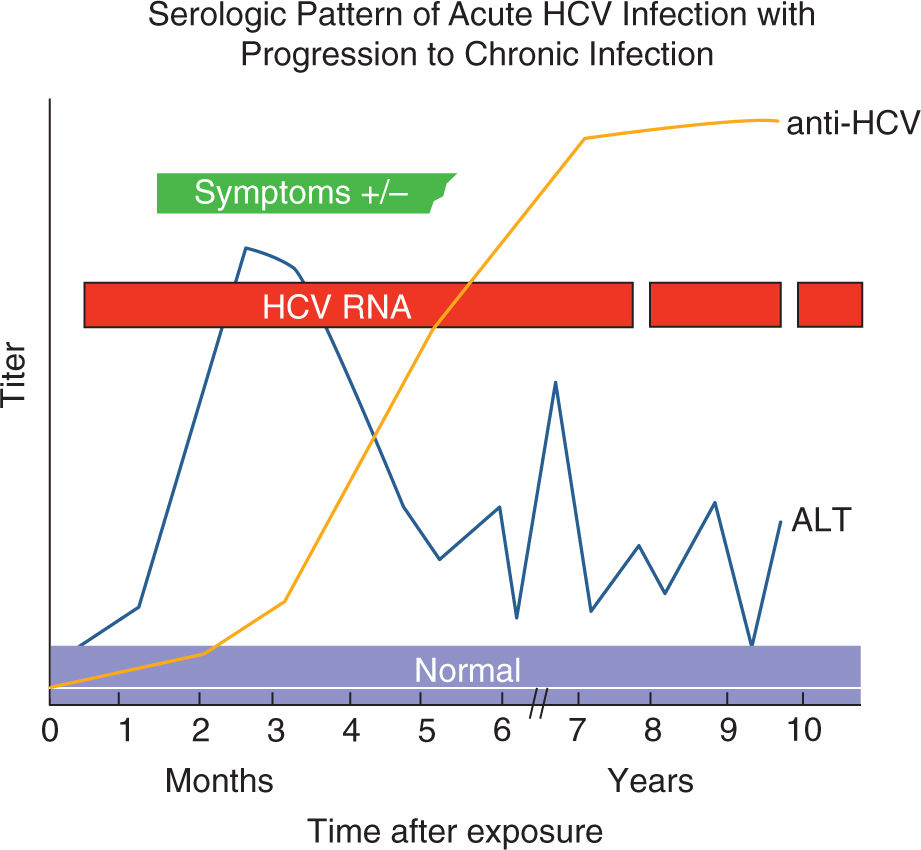
Arslanoglu i, cetin b, isguven p, karavus m. anti-hbs response to standard hepatitis b vaccination in children and adolescents with diabetes mellitus. j pediatric end & metabolism 2002;15(4):389-95. bouter kp, diepersloot rj, wismans pj, et al. humoral immune response to a yeast-derived hepatitis b vaccine in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus. Vaccination is most cost effective for adults with diabetes for ages <60 years a preventable outcomes consist of acute hepatitis, fulminant hepatitis, chronic hepatitis, cirrhosis, hepatocellular carcinoma, liver transplantation, death. Print version cdc-pdf [36 pages] acip-vfc resolution. archived hepatitis b immunization publications. for your convenience, these archived publications can be used for historical and research purposes. mmwr, december 23, 2011, vol 60, 50 policy note: use of hepatitis b vaccine for adults with diabetes mellitus. print version cdc-pdf [1. 07mb.
The vaccination of all adults with diabetes aged 19–60 years is said to be moderately cost-effective, and forms the basis of cdc recommendations for this cohort [ 6 8 ]. however, it is unclear at present time of what the value of hepatitis b vaccination for diabetic individuals sixty years or older. Since the hepatitis b virus can be transmitted via blood or other bodily fluids, people living with diabetes are at an increased risk of contracting hepatitis b. in fact, one study found that people cdc diabetes hepatitis b living with diabetes between the ages of 23-59 have an approximately two-fold increased risk of hep b infection compared to those without diabetes. Hepatitisb vaccine recommended for people with diabetes. cdc and acip recommend hepatitis b vaccination for all unvaccinated adults with diabetes who are younger than 60 years of age. vaccination should occur as soon as possible after diagnosis of diabetes; vaccination should also be given to adults diagnosed with diabetes in the past.
The hepatitis b virus can survive outside the body at least a week. during that time, the virus can still cause infection if it enters the body of a person who is not infected. how has transmission occurred in healthcare facilities? cdc has investigated numerous hepatitis b outbreaks in people with diabetes in assisted living, long-term. Cdc recommends hepatitis b vaccination for all unvaccinated adults with diabetes younger than 60 years of age. • if you think you have already been vaccinated, confirm with your doctor. • the hepatitis b vaccine is given as a series of 3 shots over a cdc diabetes hepatitis b period of 6 months (0, 1, 6 month schedule). Introduction. recent evidence show that hepatitis b infection occurs more frequently among individuals with type 2 diabetes than the general population [1–3]. the odds for developing acute hepatitis b for individuals with diabetes is said to be as much as twice that for non-diabetics. Diabetes and hepatitis b vaccination information for diabetes educators pdf icon [1. 4mb, 2 pages] give birth to the end of hep b external icon immunization action coalition.
Use of hepatitis b vaccination for adults with diabetes mellitus: recommendations of the advisory committee on immunization practices (acip) hepatitis b virus (hbv) causes acute and chronic infection of the liver leading to substantial morbidity and mortality. Imazeki f, yokosuka o, fukai k, et al. prevalence of diabetes mellitus and insulin resistance in patients with chronic hepatitis c: comparison with hepatitis b virus-infected and hepatitis c virus-cleared patients. liver int. 2008; 28:355–362. doi: 10. 1111/j. 1478-3231. 2007. 01630. x. Centers for disease control and prevention (cdc). use of hepatitis b vaccination for adults with diabetes mellitus: recommendations of the advisory committee on immunization practices (acip). mmwr morb mortal wkly rep 2011; 60: 1709 1711. Cdc and acip recommend hepatitis b vaccination for all unvaccinated adults with diabetes who are younger than 60 years of age. vaccination should occur as soon as possible after diagnosis of diabetes; vaccination should also be given to adults diagnosed with diabetes in the past. acip recommends hepatitis b vaccination occur at the discretion of the health care provider for unvaccinated adults with diabetes who are 60 years and older.
An infection can complicate diabetes self-management, increasing the risk of hospitalization and mortality. the ada 2019 standards of medical care in diabetes and the centers for disease control and cdc diabetes hepatitis b prevention (cdc) provide vaccination recommendations for adults with diabetes, specifically influenza, pneumococcal, and hepatitis b vaccinations. Hepatitisb infection impacts an estimated 850,000 people in the united states, and according to recent data from the u. s. centers for disease control and prevention (cdc), new hepatitis b infections are on the rise. left untreated, infection with hepatitis b can lead to serious liver disease, liver cancer, and even death.


Comments
Post a Comment